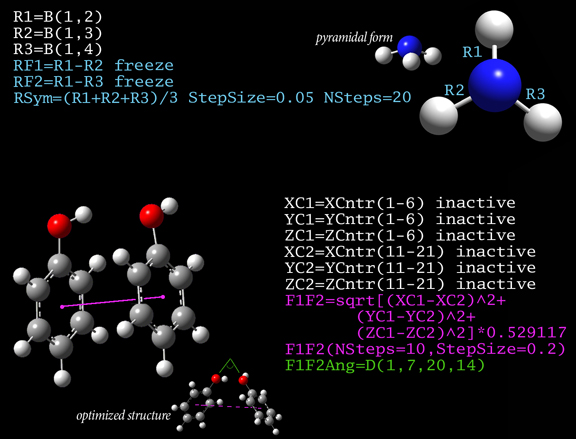
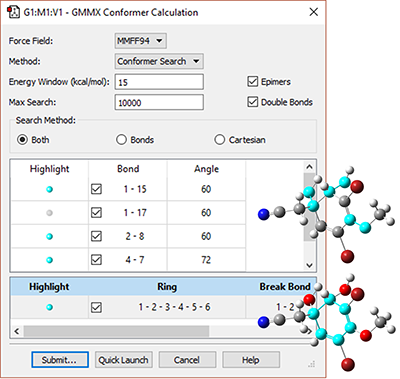
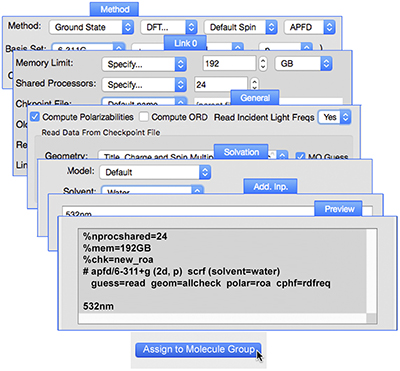
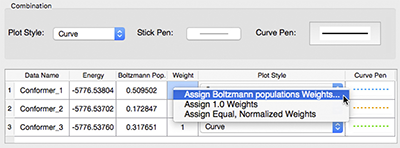
Gaussian
Gaussian for Computational Chemistry.
For nearly 40 years, the Gaussian series has been a leader in electronic structure programs. The latest version, Gaussian 16, offers cutting-edge methods and capabilities that allow researchers to tackle increasingly complex molecular systems across diverse areas of chemistry. When combined with GaussView 6, which provides a comprehensive suite of building and visualization tools, the Gaussian environment sets the standard for computational chemistry. This suite empowers researchers with powerful features and innovations, solidifying Gaussian’s position as the premier choice for scientists worldwide.
- Cutting-edge electronic structure methods: Gaussian 16 offers state-of-the-art capabilities for studying complex molecules.
- Broad applicability: The program can be applied to diverse areas of chemistry.
- Scalability: Gaussian 16 allows researchers to tackle increasingly larger molecular systems.
- Integrated visualization: Combined with GaussView 6, Gaussian provides a seamless workflow from building molecules to visualizing results.
- Established leader: With a 40-year legacy, Gaussian is the trusted choice for computational chemists around the world.
An Introduction to Gaussian and GaussView
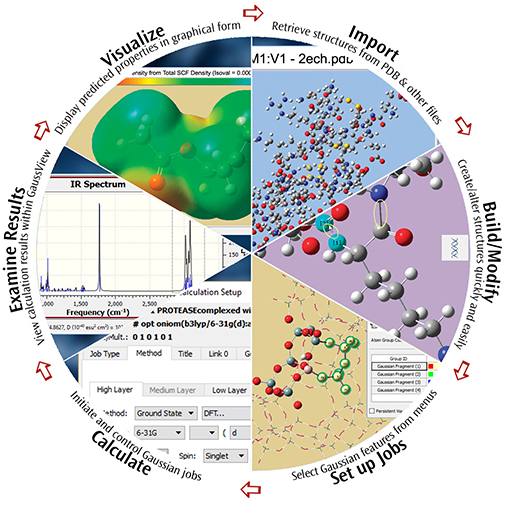
Continuing the nearly 40-year tradition of the Gaussian series of electronic structure programs, Gaussian 16 offers new methods and capabilities which allow you to study ever larger molecular systems and additional areas of chemistry. GaussView 6 offers a rich set of building and visualization capabilities. We highlight some of the most important features on this page.
Click To Read About Exploring New Substances and Environments: Green Fluorescent Protein.

About Gaussian
Capabilities of Gaussian
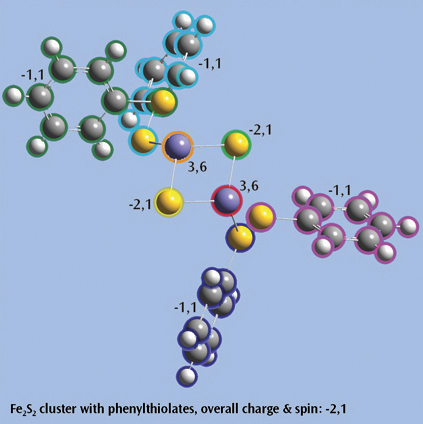
Gaussian 16 is the latest version of the Gaussian series of electronic structure programs, used by chemists, chemical engineers, biochemists, physicists and other scientists worldwide. Gaussian 16 provides a wide-ranging suite of the most advanced modeling capabilities available. You can use it to investigate the real-world chemical problems that interest you, in all of their complexity, even on modest computer hardware.
Read More To Explore The Capabilities and What You Will Receive Within Your Gaussian Environment Here.
GaussView 6
The most advanced and powerful graphical interface.
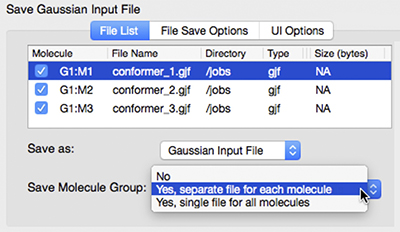
GaussView 6 is the latest iteration of a graphical interface used with Gaussian. It aids in the creation of Gaussian input files, enables the user to run Gaussian calculations from a graphical interface without the need for using a command line instruction, and helps in the interpretation of Gaussian output (e.g., you can use it to plot properties, animate vibrations, visualize computed spectra, etc.).
Please Click Here And Learn More On The GaussView 6 GUI.
Chemistry In Solution
Chemistry in Solution
A substantial part of interesting chemical processes occurs in solution. The presence of a solvent can change molecular structure, molecular properties, the relative energies of isomers, the relative abundances of conformations, and many other important factors. Chemistry can also change from one solvent to another.
All available molecular properties can be predicted in solution. Solvation can be included in calculations on both ground state and excited state systems and in ONIOM models.
Click To Read About Chemical Processes That Occur In Solution In Gaussian.
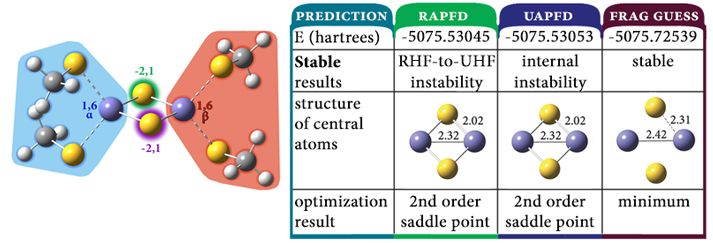
Investigating Large Systems
Investigating Large Systems with ONIOM
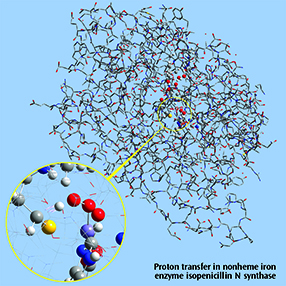
The wide variety of theoretical methods and basis sets available in Gaussian include many that are highly accurate. Unfortunately, such model chemistries scale unfavorably with the size of the molecule, resulting in a practical limit on how large a system can be studied. Gaussian’s ONIOM facility provides a means for overcoming these limitations, allowing you to study large systems that would otherwise be out of reach to all but the cheapest methods.
Read More Here On Large Systems With Gaussian and ONIOM.
Modeling Spectroscopy
Modeling Spectroscopy
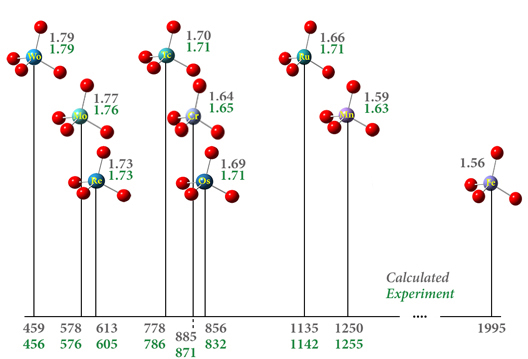
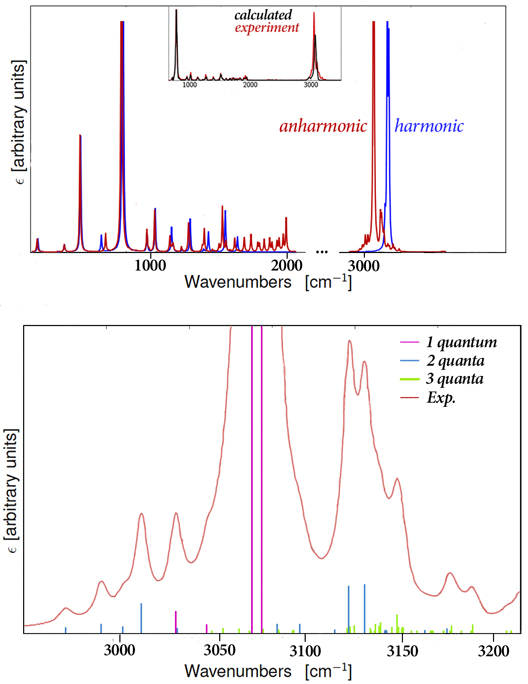
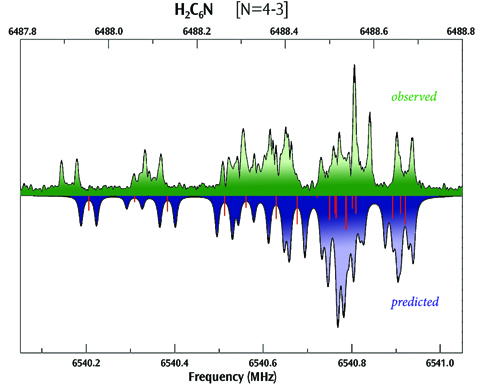
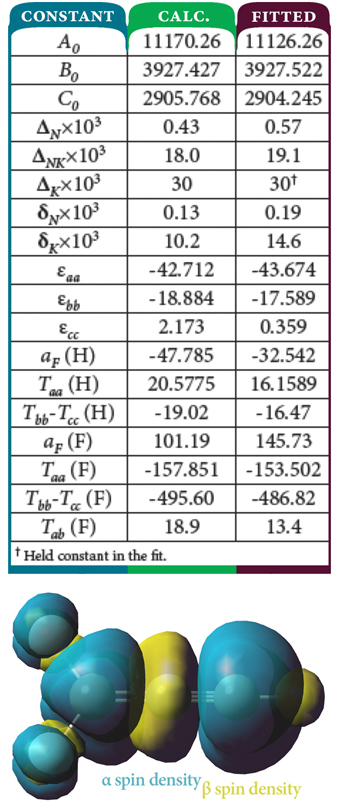
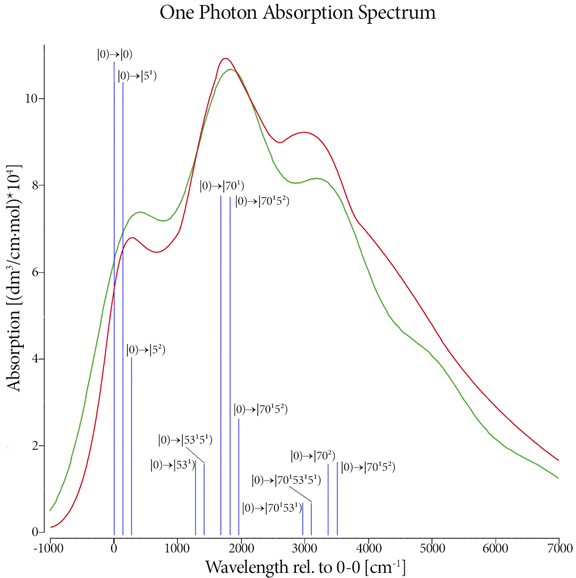
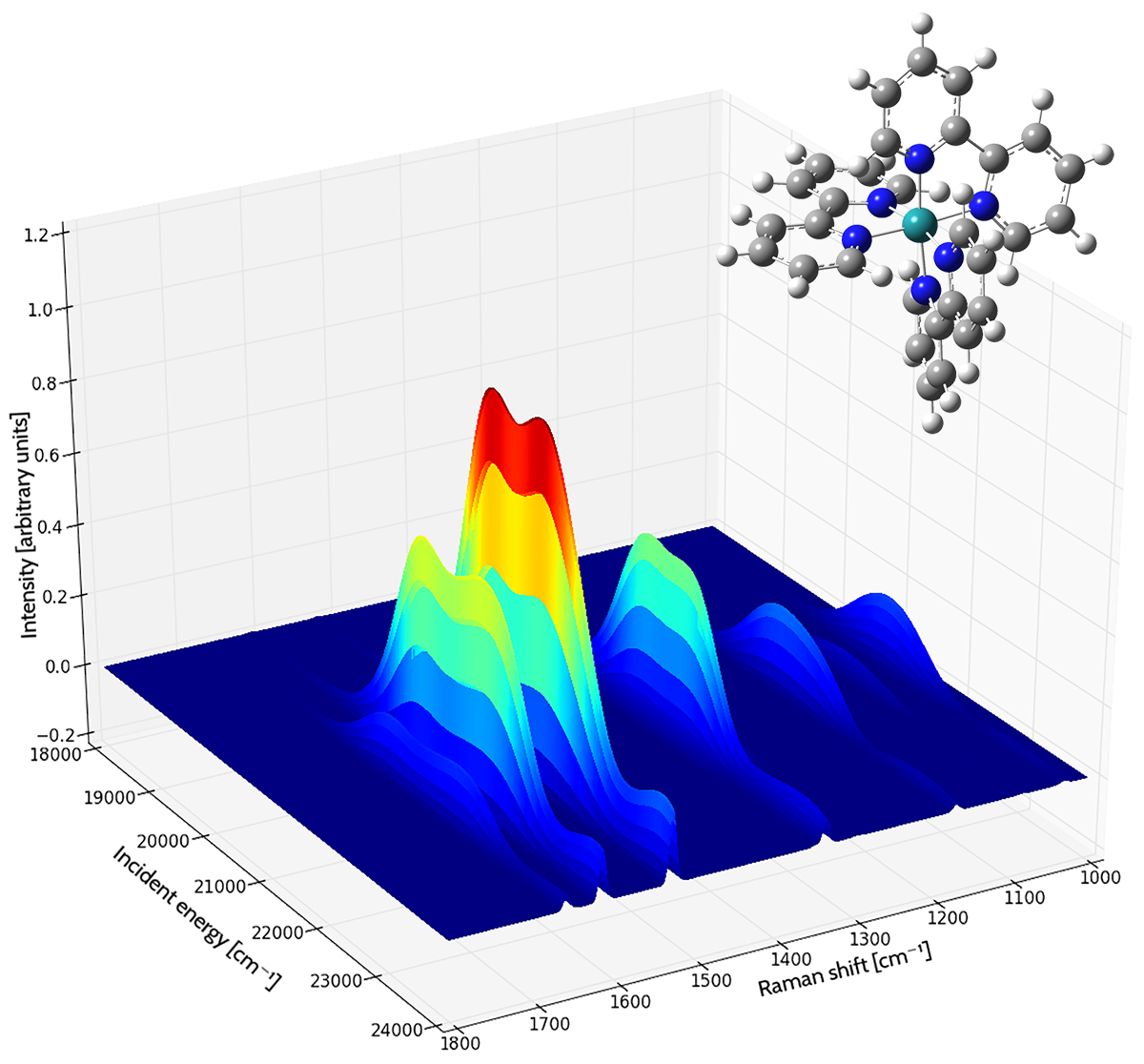
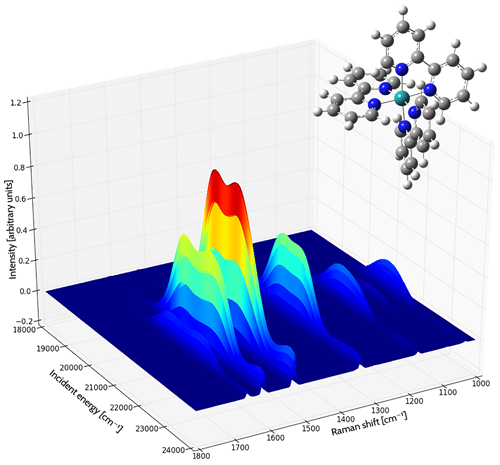
Spectroscopy is a fundamental tool for investigating molecular structures and properties. However, observed spectra are often difficult to interpret. The results of electronic structure calculations can be vital to this process. For example, predicted spectra can be examined in order to determine peak assignments in observed spectra as well as to compare peak locations and intensities with experimental data. Gaussian 16 can also compute relevant spectroscopic constants and related molecular properties with excellent accuracy. This combination of experimental observation and theoretical computation can yield very accurate structural and spectral data for compounds of interest.
Read More Here To Fully Explorer Spectroscopy.
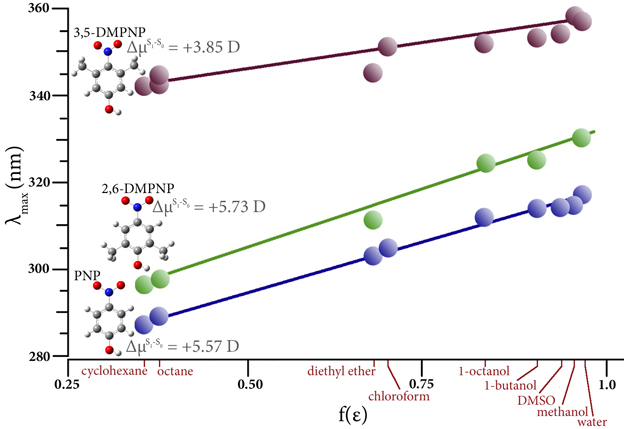
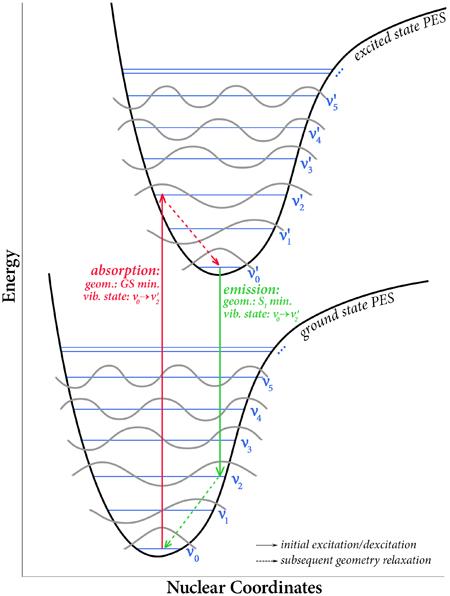
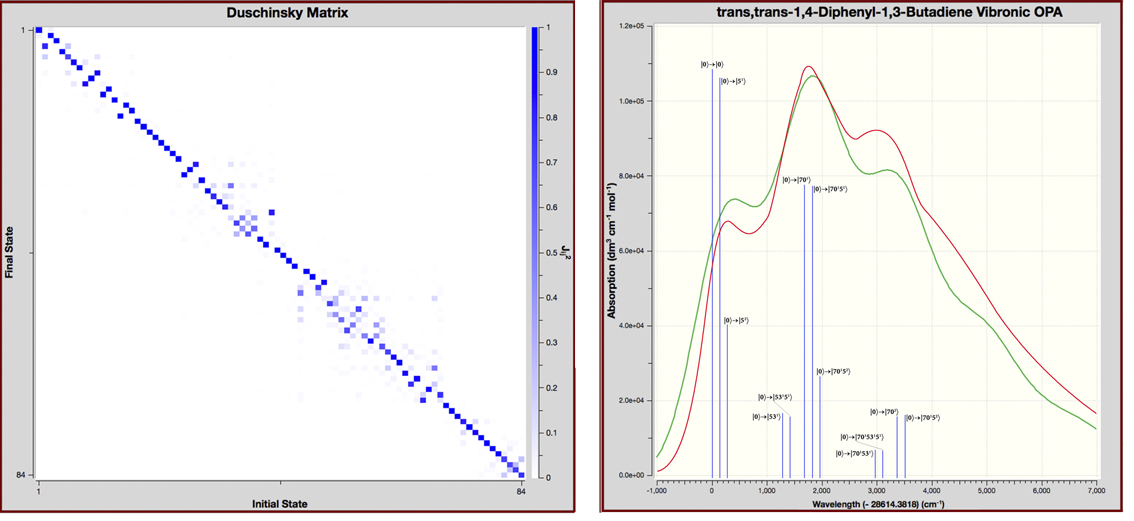
Excited States
Studying Excited State Chemistry
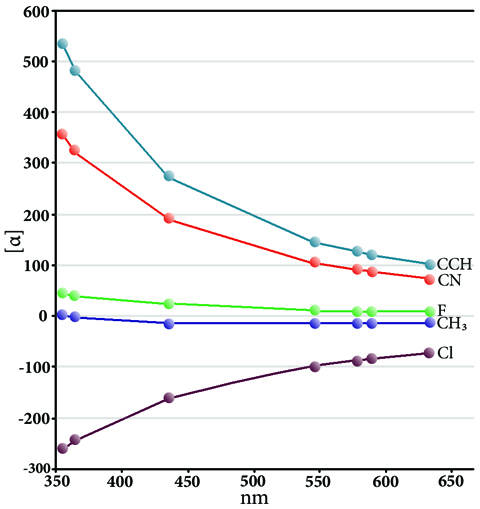
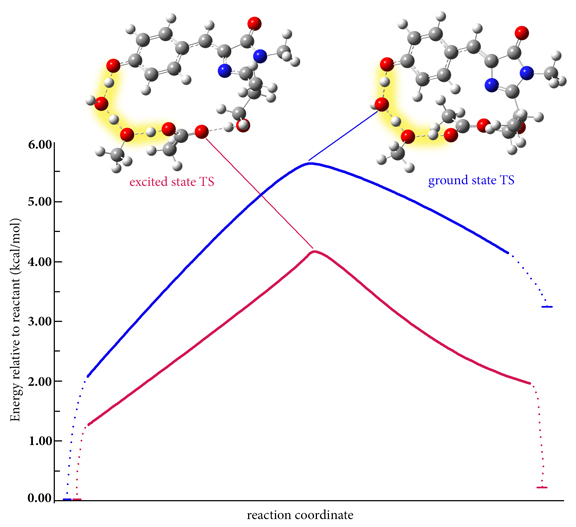
Excited states are relevant to the study of a wide variety of phenomenon, including photosynthesis, photodecomposition, photochemical generation of electricity, perception of light in animals, fluorescence, bioluminescence, and more. Gaussian can calculate UV-Visible spectra, model processes and reactions on excited state potential energy surfaces and predict vibronic absorption and emission spectra. Calculations can be performed in the gas phase and in solution.
Read On To Learn how Gaussian Aides WIth The Excited State Here.
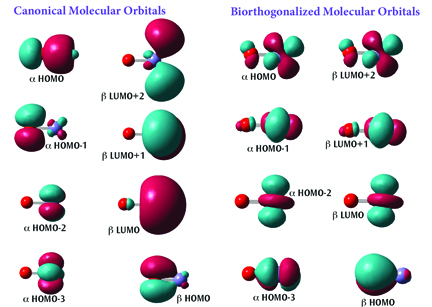
Powerful Capabilities, Yet Simple to Use
Powerful Capabilities, Yet Simple to Use
Gaussian 16 makes running even quite complex calculations very simple to set up and specify. We highlight some of the features which accomplish this goal in this section.
Learn About All The Power And Capabilities Here.
Application Examples
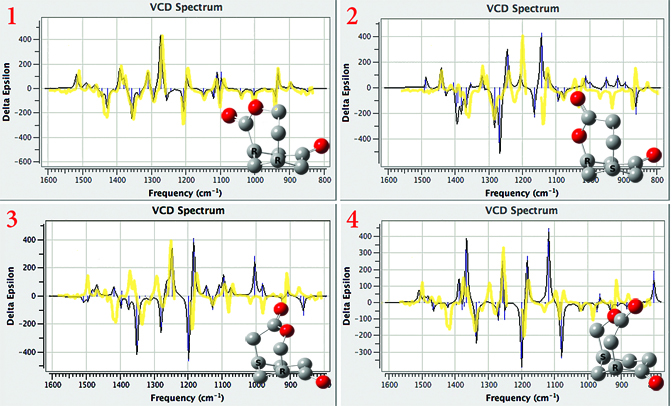
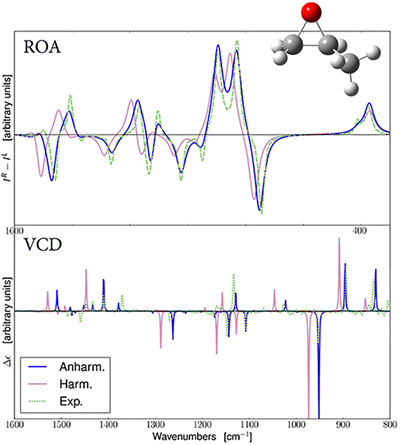
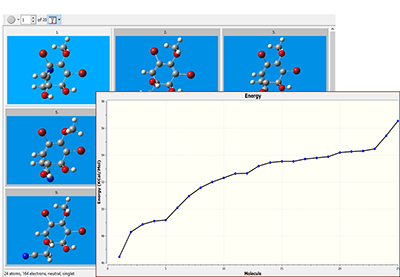
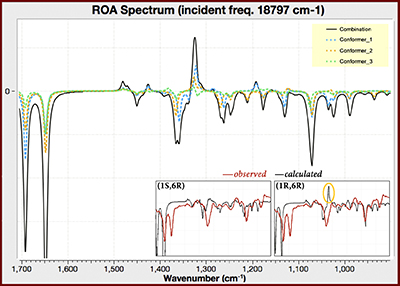
Application Example: ROA Spectrum of Aeroplysinin-1
Aeroplysinin-1 is a brominated compound that is of interest as an antiangiogenic drug [NietoOrtega11]. Here we will briefly discuss how Gaussian and GaussView can be used to predict its ROA spectrum in order to determine the molecule’s absolute configuration.
Click To See Different Examples.
Ease of Use
Ease of Use Features
Discover the ease of use with Gaussian, where intuitive interfaces and streamlined workflows simplify complex computational tasks. Effortlessly build, visualize, and analyze molecular systems with user-friendly tools designed for both novice and experienced researchers.
Read About The Ease Of Use Features Within Gaussian and GausView Here.
Features At A Glance
Working with Gaussian 16 Features at a Glance
Experience the cutting-edge advancements in Gaussian, featuring enhanced algorithms for researching larger molecular systems and exploring new areas of drug development. The latest version offers powerful new methods and capabilities that push the boundaries of computational chemistry.
View The Features At A Glance List: Click Here
Unlock the future of scientific discovery by starting your own computational chemistry environment. With state-of-the-art tools like Gaussian, you can dive into advanced molecular research, optimize drug candidates, and explore new chemical compounds with unparalleled precision and efficiency. Embrace the power of high-performance computing to accelerate your research, reduce costs, and stay at the forefront of innovation. Start your journey today and transform the way you conduct chemical research. with your own computational chemistry software environment.
Start Today


Why Gaussian?
Here are six compelling reasons to choose our Gaussian Platform for your computational chemistry and drug development needs:
Cost Efficiency
Computational chemistry and in silico labs significantly reduce the costs associated with reagents, materials, and physical lab space required for wet labs.
Speed
Simulations and computational models can rapidly screen and optimize drug candidates, accelerating the initial phases of drug development compared to the slower pace of wet lab experiments.
Safety
in silico methods eliminate the risks associated with handling hazardous chemicals and conducting potentially dangerous experiments, ensuring a safer research environment.
Scalability
Computational models can easily be scaled to study larger and more complex molecular systems, which may be challenging or impractical in wet labs.
Predictive Power
Advanced algorithms and simulations provide detailed insights into molecular interactions and predict properties and behaviors that may not be easily observable in wet lab experiments.
Resource Conservation
in silico labs conserve valuable resources, including rare or expensive materials, by allowing extensive testing and optimization in a virtual environment before any physical trials.

Discovering. Improving.
Drug Design Perfected.
Quick Links
A Guide To in silico Drug Design
Computational Methods in Drug Discovery
P: 910.756.6106
F: 279.300.3241